Realtime Transcription - Python
Realtime transcription allows you to transcribe audio content into text in real-time during a session. This guide will walk you through using the start_transcription() and stop_transcription() functions to manage realtime transcription in your server.
Moreover, VideoSDK offers flexibility in configuring real-time transcription, allowing you to set up webhooks for this purpose.
Integrating Realtime Transcription Feature
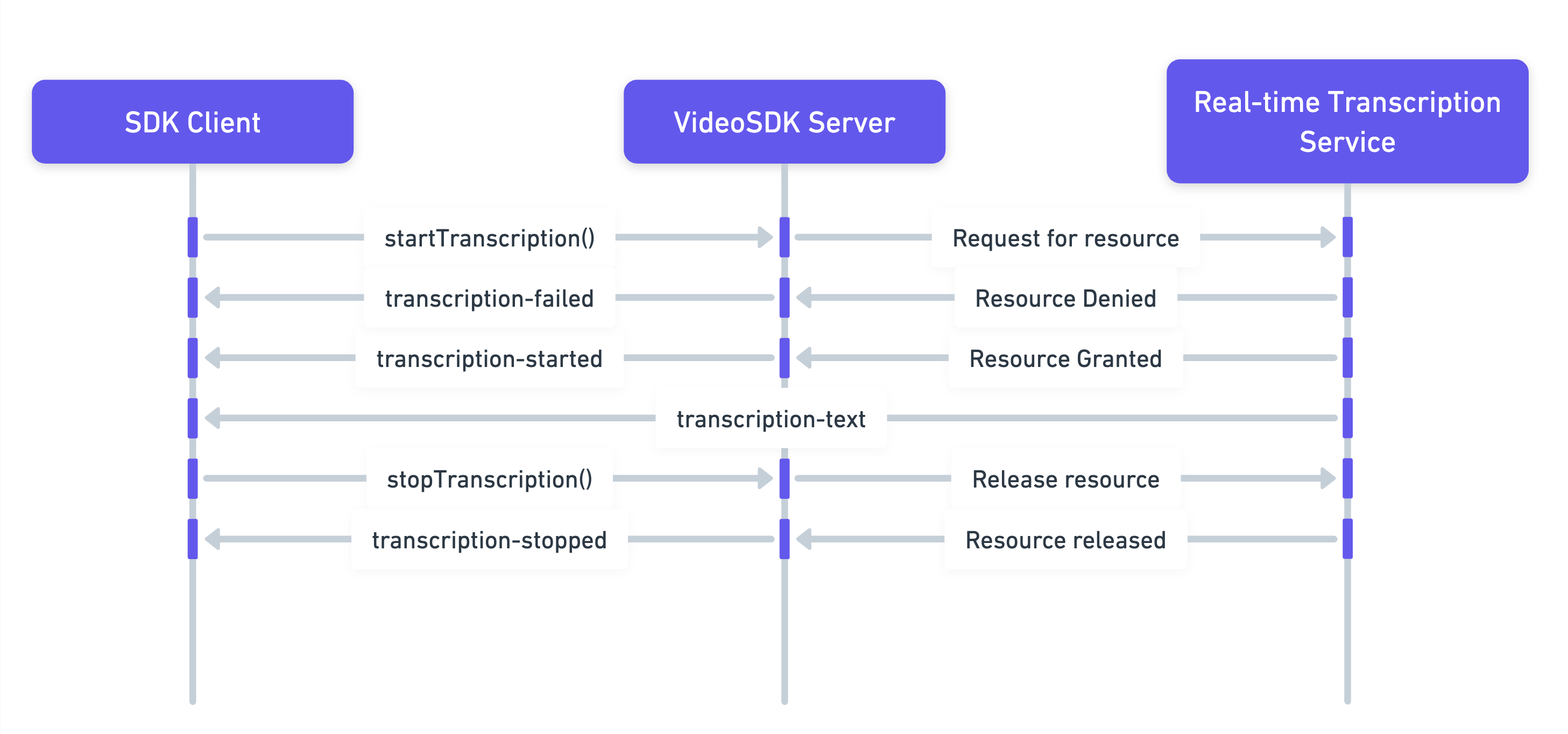
The above image represents,
-
Start Transcription: The SDK Client initiates real-time transcription using the
startTranscriptionmethod. -
Resource Acquisition: VideoSDK server requests necessary resources from transcription service.
- If the request is denied, the server sends a
transcription-failedevent to the SDK Client. - If the request is successful, the server sends a
transcription-startedevent to the client, indicating that transcription has begun.
- If the request is denied, the server sends a
-
Transcription Data: As transcription progresses, the client receives
transcription-textevent with data such as the text itself, participant ID, and timestamp. -
Stop Transcription: When the client decides to stop transcription, it informs the VideoSDK server to release resources.
- The server then sends a
transcription-stoppedevent to confirm that transcription has ended and resources are released.
- The server then sends a
Step 1: Configure Realtime Transcription
- In this step, we set up the configuration for realtime transcription. We define the webhook URL where the webhooks will be received.
# Configurations for Realtime Transcription
webhook_url = "https://www.example.com"
Step 2: Listen for the transcription events
- Here, we configure the callback methods for transcription events.
from videosdk import Meeting, MyMeetingEventHandler
class MyMeetingEventHandler(MeetingEventHandler):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def on_transcription_state_changed(self, data):
print("transcription state changed", data)
def on_transcription_text(self, data):
print("transcription text", data)
Step 3: Start realtime transcription
- Initiate the realtime transcription using the
start_transcription()method.
transcription_config = TranscriptionConfig(
webhook_url = webhook_url
summary=SummaryConfig(
enabled=True,
prompt="Write summary in sections like Title, Agenda, Speakers, Action Items, Outlines, Notes and Summary"
)
)
meeting.start_transcription(transcription_config)
Step 4: Stop realtime transcription
- Terminate the realtime transcription using the
stop_transcription()method.
meeting.stop_transcription()
Example
- The following python code snippet allows you to start and stop realtime transcription with just a second.
import asyncio
from videosdk import (
MeetingConfig,
VideoSDK,
MeetingEventHandler,
SummaryConfig,
TranscriptionConfig
)
VIDEOSDK_TOKEN = "<VIDEOSDK_TOKEN>"
MEETING_ID = "<MEETING_ID>"
NAME = "<NAME>"
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
class MyMeetingEventHandler(MeetingEventHandler):
def on_transcription_state_changed(self, data):
print(f"===== transcription state changed -> {data} =====")
def on_transcription_text(self, data):
print(f"===== transcription text -> {data} =====")
async def main():
meeting = VideoSDK.init_meeting(**MeetingConfig(
meeting_id=MEETING_ID,
name=NAME,
mic_enabled=True,
webcam_enabled=True,
token=VIDEOSDK_TOKEN,
))
meeting.add_event_listener(MyMeetingEventHandler())
meeting.join()
await asyncio.sleep(5)
meeting.start_transcription(TranscriptionConfig(
summary=SummaryConfig(
enabled=True,
prompt="Write summary in sections like Title, Agenda, Speakers, Action Items, Outlines, Notes and Summary"
)
))
await asyncio.sleep(60)
meeting.stop_transcription()
if __name__ == "__main__":
loop.run_until_complete(main())
loop.run_forever()
You can access a summary of your realtime transcription using the Fetch Realtime Transcription API.
API Reference
The API references for all the methods utilized in this guide are provided below.
Got a Question? Ask us on discord

