Agent Session
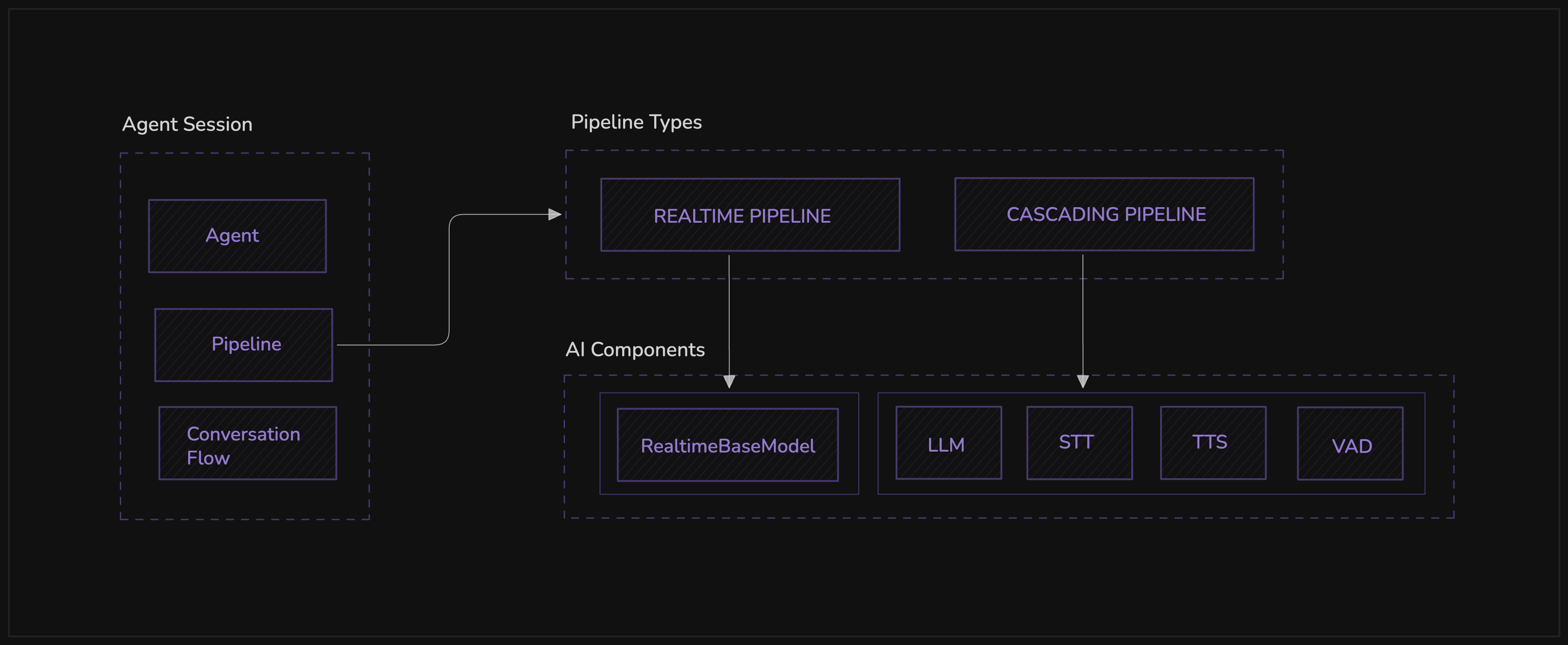
The AgentSession is the central orchestrator that integrates the Agent, Pipeline, and optional ConversationFlow into a cohesive workflow. It manages the complete lifecycle of an agent's interaction within a VideoSDK meeting, handling initialization, execution, and cleanup.
Core Features
- Component Orchestration: Unifies agent, pipeline, and conversation flow components.
- Lifecycle Management: Handles session start, execution, and cleanup
State Management
The AgentSession provides comprehensive state tracking for both users and agents, automatically emitting state change events for real-time monitoring.
The state management features and enhanced methods (reply(), interrupt()) are available in versions above v0.0.35.
User States
- IDLE - User is not actively speaking or listening
- SPEAKING - User is currently speaking
- LISTENING - User is actively listening to the agent
Agent States
- STARTING - Agent is initializing
- IDLE - Agent is ready and waiting
- SPEAKING - Agent is currently generating speech
- LISTENING - Agent is processing user input
- THINKING - Agent is processing and generating response
- CLOSING - Agent is shutting down
State Event Monitoring
State changes are automatically emitted as events that you can listen to:
def on_user_state_changed(data):
print("User state:", data)
def on_agent_state_changed(data):
print("Agent state:", data)
session.on("user_state_changed", on_user_state_changed)
session.on("agent_state_changed", on_agent_state_changed)
Constructor Parameters
AgentSession(
agent: Agent,
pipeline: Pipeline,
conversation_flow: Optional[ConversationFlow] = None,
wake_up: Optional[int] = None
)
Agent
Your custom agent implementation
Pipeline
Either RealTimePipeline or CascadingPipeline
Conversation Flow
Optional conversation state management
Wake-Up Call
Wake-up call automatically triggers actions when users are inactive for a specified period of time, helping maintain engagement.
# Configure wake-up timer
session = AgentSession(
agent=MyAgent(),
pipeline=pipeline,
wake_up=10 # Trigger after 10 seconds of inactivity
)
# Set callback function
async def on_wake_up():
await session.say("Are you still there? How can I help?")
session.on_wake_up = on_wake_up
Important: If a wake_up time is provided, you must set a callback function before starting the session. If no wake_up time is specified, no timer or callback will be activated.
Basic Usage
To get an agent running, you initialize an AgentSession with your custom
Agent and a configured Pipeline. The session handles the underlying
connection and data flow.
Example Implementation:
- Real-time Pipeline
- Cascading Pipeline
from videosdk.agents import AgentSession, Agent, WorkerJob, JobContext, RoomOptions
from videosdk.plugins.openai import OpenAIRealtime
from videosdk.agents import RealTimePipeline
class MyAgent(Agent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(instructions="You are a helpful meeting assistant.")
async def on_enter(self):
await self.session.say("Hello! How can I help you today?")
def setup_state_monitoring(self):
def on_user_state_changed(data):
print(f"User state changed to: {data['state']}")
def on_agent_state_changed(data):
print(f"Agent state changed to: {data['state']}")
self.session.on("user_state_changed", on_user_state_changed)
self.session.on("agent_state_changed", on_agent_state_changed)
async def start_session(ctx: JobContext):
model = OpenAIRealtime(model="gpt-4o-realtime-preview")
pipeline = RealTimePipeline(model=model)
session = AgentSession(
agent=MyAgent(),
pipeline=pipeline
)
await ctx.connect()
await session.start()
# Session runs until manually stopped or meeting ends
def make_context():
return JobContext(
room_options=RoomOptions(
room_id="your-room-id",
auth_token="your-auth-token",
name="Assistant Bot"
)
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
job = WorkerJob(entrypoint=start_session, jobctx=make_context)
job.start()
from videosdk.agents import AgentSession, Agent, WorkerJob, JobContext, RoomOptions
from videosdk.plugins.openai import OpenAISTT, OpenAITTS, OpenAILLM
from videosdk.agents import CascadingPipeline
class MyAgent(Agent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(instructions="You are a helpful meeting assistant.")
async def on_enter(self):
await self.session.say("Hello! How can I help you today?")
def setup_state_monitoring(self):
def on_user_state_changed(data):
print(f"User state changed to: {data['state']}")
def on_agent_state_changed(data):
print(f"Agent state changed to: {data['state']}")
self.session.on("user_state_changed", on_user_state_changed)
self.session.on("agent_state_changed", on_agent_state_changed)
async def start_session(ctx: JobContext):
# Configure individual components
stt = OpenAISTT(model="whisper-1")
llm = OpenAILLM(model="gpt-4")
tts = OpenAITTS(model="tts-1", voice="alloy")
pipeline = CascadingPipeline(
stt=stt,
llm=llm,
tts=tts
)
session = AgentSession(
agent=MyAgent(),
pipeline=pipeline
)
await ctx.connect()
await session.start()
# Session runs until manually stopped or meeting ends
def make_context():
return JobContext(
room_options=RoomOptions(
room_id="your-room-id",
auth_token="your-auth-token",
name="Assistant Bot"
)
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
job = WorkerJob(entrypoint=start_session, jobctx=make_context)
job.start()
Development and Testing Features
The AgentSession supports several modes for development, testing, and user engagement:
Playground Mode
Playground mode provides a web-based interface for testing your agent without building a separate client application.
Usage
To activate playground mode, simply set playground: True in your RoomOptions for JobContext.
from videosdk.agents import RoomOptions, JobContext, WorkerJob
async def entrypoint(ctx: JobContext):
# Your agent implementation here
# This is where you create your pipeline, agent, and session
pass
def make_context() -> JobContext:
room_options = RoomOptions(
room_id="<meeting_id>",
name="Test Agent",
playground=True # Enable playground mode
)
return JobContext(room_options=room_options)
if __name__ == "__main__":
from videosdk.agents import WorkerJob
job = WorkerJob(entrypoint=entrypoint, jobctx=make_context)
job.start()
When enabled, the playground URL is automatically displayed in your terminal for easy access.
Note: Playground mode is designed for development and testing purposes. For production deployments, ensure playground mode is disabled to maintain security and performance.
Console Mode
Console mode allows you to test your agent directly in the terminal using your microphone and speakers, without joining a VideoSDK meeting.
Usage
To use console mode, simply add the console argument when running your agent script:
python main.py console
The console will display:
- Agent speech output
- User speech input
- Various latency metrics (STT, TTS, LLM,EOU)
- Pipeline processing information
This flexibility allows you to use the same agent code for both development and production environments.
Session Lifecycle Management
The AgentSession provides methods to control the agent's presence and behavior in the meeting.
start(**kwargs)
Initializes and starts the agent session. Sets up MCP tools, metrics collection, pipeline, and calls agent's on_enter() hook.
say(message: str)
Sends a message from the agent to the meeting participants. Allows the agent to communicate with users in the meeting.
close()
Gracefully shuts down the session. Finalizes metrics collection, cancels wake-up timer, and calls agent's on_exit() hook.
leave()
Leaves the meeting without full session cleanup. Provides a quick exit option while maintaining session state.
reply(instructions, wait_for_playback)
Generate agent responses using instructions and current chat context. Includes playback control and prevents concurrent calls.
interrupt()
Immediately interrupt the agent's current operation, stopping speech generation and LLM processing for emergency stops or user interruptions.
Example of Managing the Lifecycle:
import asyncio
from videosdk.agents import AgentSession, Agent, WorkerJob, JobContext, RoomOptions
from videosdk.plugins.openai import OpenAIRealtime
from videosdk.agents import RealTimePipeline
class MyAgent(Agent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(instructions="You are a helpful meeting assistant.")
# LIFECYCLE: Agent entry point - called when session starts
async def on_enter(self):
await self.session.say("Hello! How can I help you today?")
# LIFECYCLE: Agent exit point - called when session ends
async def on_exit(self):
print("Agent is leaving the session")
@function_tool
async def provide_summary(self) -> str:
"""Provide a conversation summary using the new reply method"""
await self.session.reply("Let me summarize our conversation so far...")
return "Summary provided"
@function_tool
async def stop_speaking(self) -> str:
"""Emergency stop functionality"""
await self.session.interrupt()
return "Agent stopped successfully"
async def run_agent_session(ctx: JobContext):
# LIFECYCLE STAGE 1: Session Creation
model = OpenAIRealtime(model="gpt-4o-realtime-preview")
pipeline = RealTimePipeline(model=model)
session = AgentSession(agent=MyAgent(), pipeline=pipeline)
try:
# LIFECYCLE STAGE 2: Connection Establishment
await ctx.connect()
# LIFECYCLE STAGE 3: Session Start
await session.start()
# LIFECYCLE STAGE 4: Session Running
await asyncio.Event().wait()
finally:
# LIFECYCLE STAGE 5: Session Cleanup
await session.close()
# LIFECYCLE STAGE 6: Context Shutdown
await ctx.shutdown()
# LIFECYCLE STAGE 0: Context Creation
def make_context() -> JobContext:
room_options = RoomOptions(room_id="your-room-id", auth_token="your-token")
return JobContext(room_options=room_options)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# LIFECYCLE ORCHESTRATION: Worker Job Management
# Creates and starts the worker job that manages the entire lifecycle
job = WorkerJob(entrypoint=run_agent_session, jobctx=make_context)
job.start()
Examples - Try Out Yourself
We have examples to get you started. Go ahead, try out, talk to agent, understand and customize according to your needs.
Got a Question? Ask us on discord

